What Is a Turnkey Asset Management Program?

Financial advisors and asset managers often turn to Turnkey Asset Management Programs (TAMPs) to help them manage clients’ accounts.
How Does Depreciation Work On a Triple Net Lease (NNN)?

Depreciation is one of the best tax deductions for real estate investing. It’s a non-cash flow expense because it doesn’t affect an investor’s bank account but can reduce taxable income.
How Is Retirement Income Taxed Per State? Part 4

While your expenses will likely decrease once you reach retirement age, many retirees don't factor in potential taxes when budgeting out what their future expenses will be. Many states choose to tax some or all retirement income. You may also live in a state that doesn't tax any type of retirement income. Here’s an overview of how some states tax income.
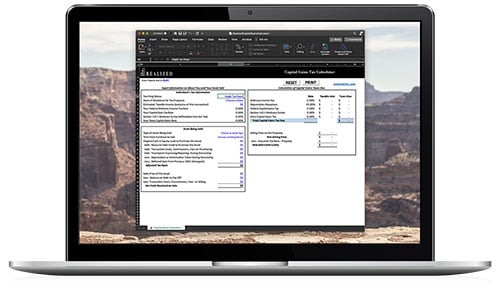
The Basics of Capital Gains

The IRS taxes different types of income at different rates. For example, when it comes to some types of capital gains, they can be taxed at more favorable rates than ordinary income. However, not all capital gains are taxed equally, and rates vary widely.
What Are The Components of a Financial Plan?

A financial plan can be an essential element of financial stability and helping you reach your financial goals.
How to Use Leverage to Invest in Real Estate

Purchasing an expensive property requires a large cash outlay. This can mean missing out on other potential opportunities and assuming full investment risk.
How is Retirement Income Taxed Per State? Part 3

Whether you have recently retired or are nearing retirement age, you'll likely be thinking about your long-term financial situation. Before you start withdrawing from your 401(k) or spending your Social Security benefits, keep in mind that your retirement income can be taxed depending on the state you live in. Each state has different laws that dictate how retirement income is taxed, some of which are detailed in the following guide.
How to Report the Sale of Rental Property

Correctly reporting the sale of rental property to the IRS is crucial since doing it wrong can result in paying the wrong amount or even having a penalty assessed, and no one wants to do that. Of course, planning for the transaction before executing it is even better than determining the correct reporting after the fact.
How to Find a Net Lease Advisor

Many real estate investors are on the hunt for net-lease properties for a variety of reasons. One such reason is because they can provide a source of passive income for a period of time, without the need to handle (or pay for) the administrative aspects of property ownership.
How is Retirement Income Taxed Per State? Part 2

If you're starting to think of retirement, you may be looking forward to moving past the daily commute and grind that are currently part of your everyday life. Whether you want to move to a different state or are content with staying where you are, the largest expense that most people have after reaching retirement age involves income taxes. However, many states keep retirement income taxes to a minimum. If you live in a state with high retirement income taxes, making a move in the near future may be beneficial. Here's a closer look at the retirement laws in 10 states and how they differ.