Does a 1031 Exchange Property Need to Be Income Producing?

The basic concept of a 1031 exchange is pretty straightforward. You “swap” one real estate property held for business or investment purposes into another “like-kind” property. When completed properly, the like-kind exchange can let you defer capital gains taxes on the sale of your original, or relinquished property.
Can Capital Losses Offset Ordinary Income?

Ordinary income is, quite simply, what you earn from providing products or services to others. The wage or salary your employer pays you falls under the category of ordinary income. Interest income from bonds also falls into this category. If you’re retired and taking withdrawals from your defined contribution plan, that withdrawal is also considered ordinary income.
What is a Limited Power of Attorney?

Assigning a power of attorney to someone authorizes that person to act on your behalf. In almost every situation, the Power of Attorney is a notarized document that specifies the breadth of the agent’s authority and the duration.
Can You Do a 1031 Exchange on Raw Land?

Completing a 1031 exchange can be a complicated journey. There are many moving parts to the exchange process, as well as important deadlines that can’t be missed.
Are Trust Funds Taxed?

A trust fund is set up like a traditional trust, but how it operates can be a little different. However, some trust funds look and operate like a living trust (or irrevocable trust). What does that mean when it comes to trust funds and taxes? Are they taxed like a living trust or an irrevocable trust?
Do Capital Losses Reduce Taxable Income?

If you take a loss on a stock, can that loss be used to reduce your taxable income? Reducing taxable income results in a lower tax bill, something most any investor would be interested in. However, there are certain rules around capital losses, and the income from those losses can be applied to. This article will dig into the gritty details of using capital losses to reduce taxable income.
What is a Multi-Asset Exchange?

Completing a 1031 exchange often means navigating a twisting, turning road that’s often fraught with speed bumps.
How Are Proceeds Held By The Qualified Intermediary?
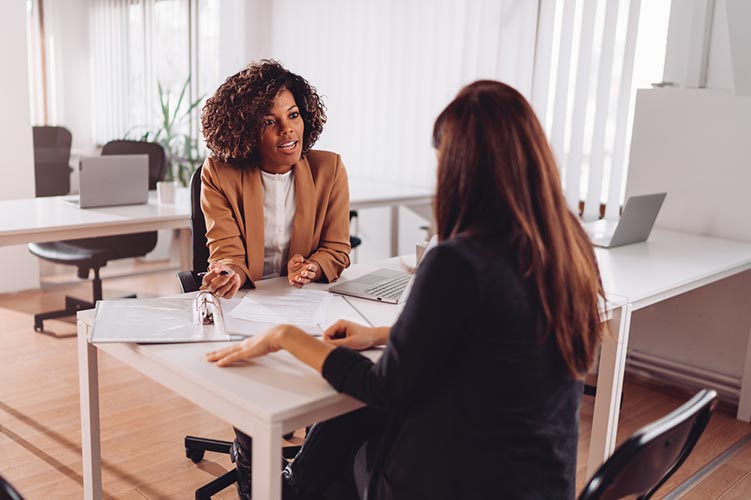

One main rule involved with the 1031 exchange process is that you, as the exchangor, are not allowed to handle any funds involved with the exchange. That job goes to the Qualified Intermediary (QI). Also known as an accommodator, the QI is an independent entity that is involved with every step of the like-kind exchange process.
Do You Have to Report Capital Losses?
Capital losses can help offset other income. This might be income from capital gains or even ordinary income. However, there are certain restrictions to these income offsets. The net capital gain or loss must be calculated as a first step. If the net is a loss, does that require reporting? Is it not like you will be taxed on a loss, right? The answer is more complex than it may first seem.
Can You Use a 1031 Exchange to Build an Investment Property?

1031 exchanges are tools that can enable real estate investors to defer the payment of capital gains taxes when they sell an investment property and reinvest the proceeds. However, if you complete a sale and purchase outside the auspices of a 1031 exchange, you will owe capital gains taxes on the difference between the adjusted basis and the sale price.


